Computer-Science
Socket programming and Protocol
0. file vs. socket
FILE
p1:
x=open("/aa/bb", ...); // find the location of file /aa/bb
// now x is pointing to the location of /aa/bb
write(x, "korea", 5); // write "korea" to the place x is pointing to
p2:
y=open("/aa/bb", ...); // find the location of file /aa/bb
// now y is pointing to the location of /aa/bb
read(y, buf, 5);
SOCKET
p1 is at 1.1.1.1:8000, p2 is at 2.2.2.2:9000
p1:
x=socket(..........);
connect(x, 2.2.2.2:9000, ..); // send connection request to 2.2.2.2:9000
// now x pointing to 2.2.2.2:9000
write(x, "korea", 5); // write "korea" to a packet which will be sent to 2.2.2.2:9000
p2:
y=socket(....);
bind(y, 2.2.2.2:9000, ..);
listen(y, ..);
y1=accept(y, ...); // response to connection request
// now y1 pointing to 1.1.1.1:8000
read(y1, buf, 5);
1. socket programming
client:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SERV_TCP_PORT 9948
#define SERV_ADDR "165.246.38.151"
void main(){
int x,y;
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr;
char buf[50];
printf("Hi, I am the client\n");
bzero((char *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family=PF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr(SERV_ADDR);
serv_addr.sin_port=htons(SERV_TCP_PORT);
//open a tcp socket
if ((x=socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0))<0){
printf("socket creation error\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("socket opened successfully. socket num is %d\n", x);
//connect to the server
if (connect(x, (struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)) < 0){
printf("can't connect to the server\n");
exit(1);
}
// send msg to the server
printf("now i am connected to the server. enter a string to send\n");
scanf("%s",buf);
write(x, buf, strlen(buf));
// read from server
printf("now reading from server\n");
y=read(x, buf, 50);
buf[y]=0;
printf("from server: %s\n", buf);
close(x); // disconect the communication
}
server:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SERV_TCP_PORT 13131
#define SERV_ADDR "165.246.38.151"
void main(){
int s1,s2, x, y;
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr, cli_addr;
char buf[50];
socklen_t xx;
printf("Hi, I am the server\n");
bzero((char *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family=PF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr(SERV_ADDR);
serv_addr.sin_port=htons(SERV_TCP_PORT);
//open a tcp socket
if ((s1=socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0))<0){
printf("socket creation error\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("socket opened successfully. socket num is %d\n", s1);
// bind ip
x =bind(s1, (struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
if (x < 0){
printf("binding failed\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("binding passed\n");
listen(s1, 5);
xx = sizeof(cli_addr);
s2 = accept(s1, (struct sockaddr *)&cli_addr, &xx);
printf("we passed accept. new socket num is %d\n", s2);
// read msg from client
printf("now reading from client\n");
y=read(s2, buf, 50);
buf[y]=0;
printf("we got %s from cli\n", buf);
// send msg to the client
printf("enter a string to send to client\n");
scanf("%s", buf);
write(s2, buf, strlen(buf));
close(s2); // disconnect the connection
close(s1); // close the original socket
}
2. socket system calls
Assume src ip=2.2.2.2, src port=2000, dest ip=3.3.3.3, dest port=3000.
x=socket(); // in client
The client system will allocate a socket structure which has
x ={my ip, my port, remote ip, remote port, input buffer, output buffer}
x is the socket id.
connect(x, &serv_addr, ...); // in client
The client system fills in the socket structure and sends a connection request packet to the server.
x={my ip=2.2.2.2, my port=2000, remote ip=3.3.3.3, remote port=3000,
input buffer={}, output buffer={}}
s1 = socket(.......); // in server
The server system will allocate a socket structure which has
s1={my ip, my port, remote ip, remote port, input buffer, output buffer}
s1 is the socket id.
s2=accept(s1, .......);
The server system sends back a response packet to the client, make another socket for actual data transmission (the original s1 socket is kept for connection purpose), and fills in the socket structure.
s1={my ip=3.3.3.3, my port=3000, remote ip={}, remote port={},
input buffer={}, output buffer={}}
s2={my ip=3.3.3.3, my port=3000, remote ip=2.2.2.2,remote port=2000,
input buffer={}, output buffer={}}
write(x, "korea", 5); // in client
The system fills in the socket x and sends the packet containing “korea” to the server.
x={my ip=2.2.2.2, my port=2000,remote ip=3.3.3.3,remote port=3000,
input buffer={},output buffer="korea"}
read(s2, buf, n); // in server
The system receives the packet from the client in s2.
s2={my ip=3.3.3.3,my port=3000, remote ip=2.2.2.2, remote port=2000,
input buffer="korea", output buffer={}}
And copy “korea” in buf.
3. protocol
1) well-known port
Internet service programs are waiting on well-known ports for service. The client can talk to these service programs by opening a socket on a well-known port and following the corresponding protocol. 21: ftp, 23: telnet, 25: smtp, 80: http, ……………………
2) SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) (rfc 2821) : for sending mail (port 25)
kchang(mail.inha.ac.kr) ==> kchang(mail.inha.ac.kr)
S: EHLO 165.246.38.219
R: 250-portal.inha.ac.kr Hello
250-TURN
.............
250 OK
S: MAIL FROM:<kchang@inha.ac.kr>
R: 250 ............... OK
S: RCPT TO:<kchang@mail.inha.ac.kr>
R: 250 ................
S: DATA
R: 354 Start mail input; end with <CRLF>.<CRLF>
S: Blah blah blah...
S: <CRLF>.<CRLF>
R: 250 ..........
S: QUIT
R: Connection closed
3) POP3 (rfc 1939) : for retrieving mail (port 110)
S: USER ****
R: +OK
S: PASS ****
R: +OK
S: stat
R: +OK 1 539
S: list
R: +OK 1 539
S: retr 1
R: +OK
mail here .........
S: quit
4) http client/server
http client(web browser):
..........
#define SERV_TCP_PORT 80
#define SERV_ADDR "165.246.10.21" // www.inha.ac.kr
..........
connect(s, ........);
write(s, "GET / HTTP/1.0\r\n\r\n", 18); // 1st msg in http protocol
read(s, buf, ..);
.............
http server(web server):
...............
s1=socket(...);
bind(s1,...); // bind on port 80
listen(s1,...);
for(;;){
s2=accept(s1, .....);
x=fork();
if (x==0){
close(s1);
read(s2, in_buf, n); // read http request
build_out_buf(in_buf, out_buf);
//find the requested html file and return with
// a proper header.
write(s2, out_buf, ....);
close(s2);
exit(0);
} else cose(s2); /
}
4. Example
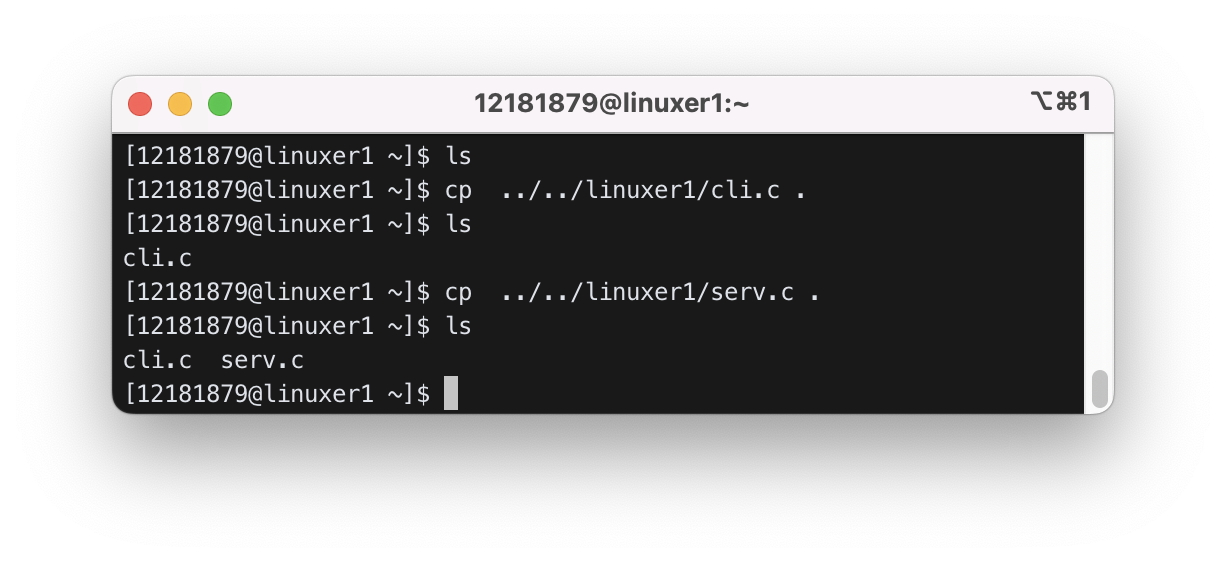
0) Copy cli.c and serv.c from linuxer1(151 server) or linnuxer2(152 server) using cp command as follows.
$ pwd
/home/sp1/12345
$ cp ../../linuxer1/cli.c .
$ cp ../../linuxer1/serv.c .
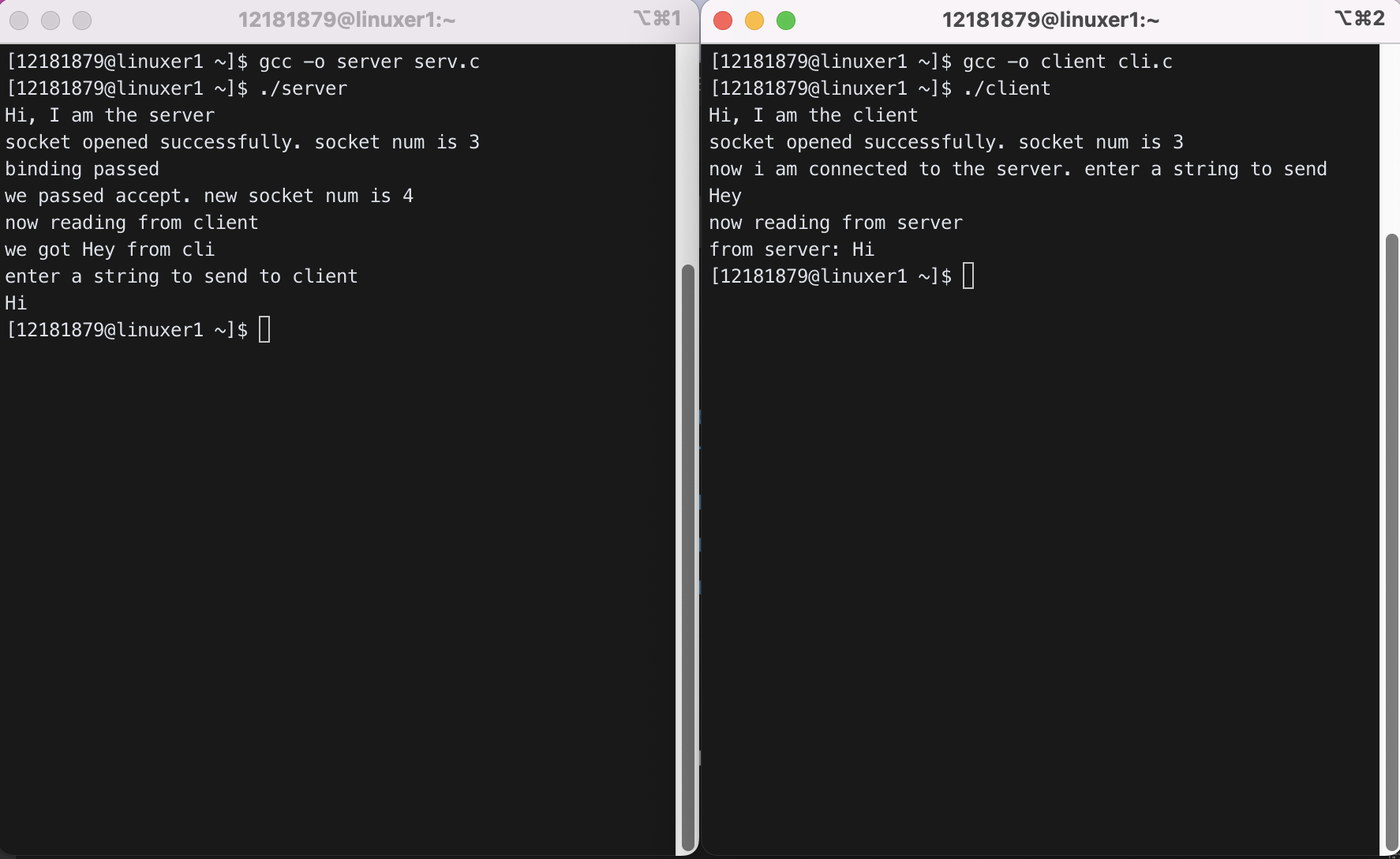
1) Adjust port and IP address for both cli.c and serv.c. SERV_ADDR in cli.c and serv.c should be the IP address of the linux server you are using. cli.c will use this SERV_ADDR to access the server while serv.c will use this SERV_ADDR to set its own IP address. Pick a port number in the range of [10000..65535]. You need two putty windows: one for the server and the other for the client. Run the server first and then the client.
(* Sometimes, you have binding failure when running the server. It happens because the server port number is blocked temporarily. Wait for 10 seconds and retry or use a different port number.)
IP 주소를 올바르게 설정해주고, 포트 번호를 35530으로 설정해주었다.
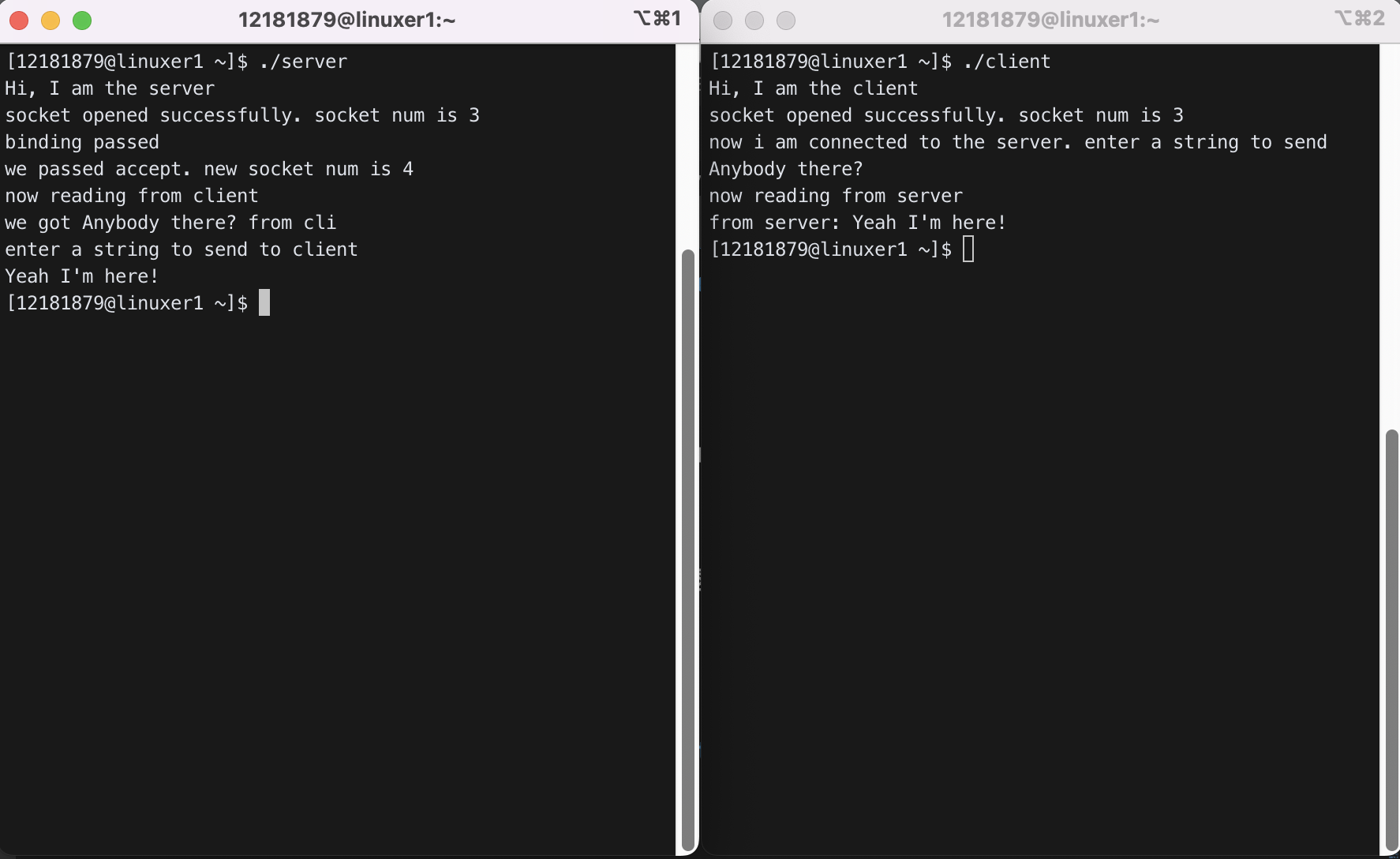
1-1) Modify cli.c and serv.c such that they can talk in sentence (not just in word as in the current implementation).
//scanf("%s",buf);
fgets(buf, 50, stdin);
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';
msg를 보내는 부분에서 기존에 있던 scanf 대신 fgets를 사용하여 공백을 포함하여 입력을 받을 수 있도록 하고, 마지막의 개행문자를 없애주었다.
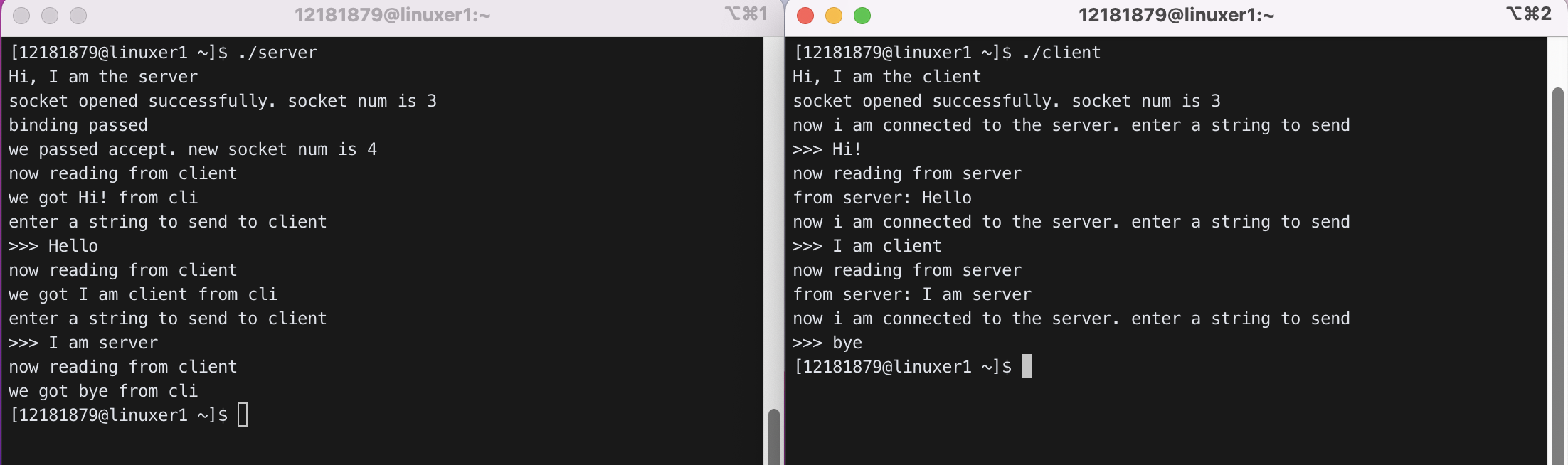
2) Modify cli.c and serv.c such that they can keep talking until the client sends “bye”. Use a finite loop.
- cli.c
- client가 server에게 메세지를 보내는 부분과 server로부터 메세지를 읽는 부분을 loop로 감싸주었다.
- server에게 메세지를 보낼 때, 메세지가 “bye”라면 loop를 탈출한다.
- 탈출한 후에는
close(x);를 통해 communication을 disconnect 시켜주었다.
for (int i; i<10; i++)
{
// send msg to the server
printf("now i am connected to the server. enter a string to send\n>>> ");
fgets(buf, 50, stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
write(x, buf, strlen(buf));
if (strcmp(buf, "bye") == 0)
break;
// read from server
printf("now reading from server\n");
y = read(x, buf, 50);
buf[y] = 0;
printf("from server: %s\n", buf);
}
close(x); // disconect the communication
- serv.c
- server도 client와 마찬가지로 client로부터 메세지를 읽어오는 부분과 client에게 메세지를 보내는 부분을 loop로 감싸주었다.
- client로부터 읽어온 메세지가 “bye”라면, loop를 탈출한다.
- 탈출한 후에는
close(s2);를 통해 client와의 connection을 disconnect하고,close(s1);를 통해 original socket을 close 한다.
for (int i; i<10; i++)
{
// read msg from client
printf("now reading from client\n");
y = read(s2, buf, 50);
buf[y] = 0;
printf("we got %s from cli\n", buf);
if (strcmp(buf, "bye") == 0)
break;
// send msg to the client
printf("enter a string to send to client\n>>> ");
fgets(buf, 50, stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
write(s2, buf, strlen(buf));
}
close(s2); // disconnect the connection
close(s1); // close the original socket
2-1) Try to talk with the other student. Note that one of you would be the client and the other the server. SERV_ADDR and SERV_TCP_PORT in cli.c should match to those in serv.c of the other student. (If you prefer to work alone, modify your cli.c such that it connects to 165.246.38.136 with port number 19924. The server program at 165.246.38.136:19924 will simply echo whatever message you send. You stop the chatting with “bye”.)
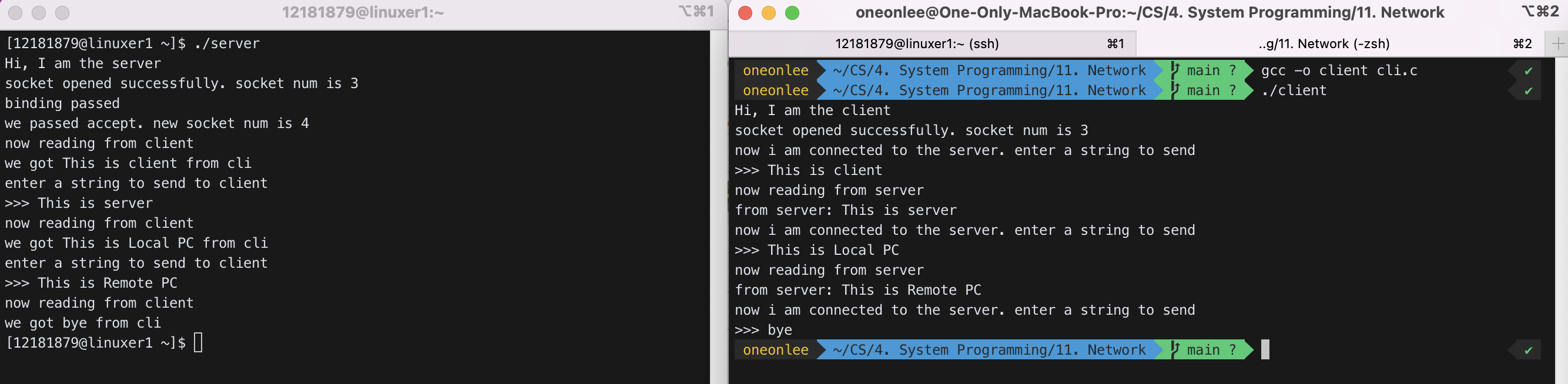
IP주소를 바꿔서 로컬PC와 원격접속PC와 통신을 하였을 때도 정상작동하였다.
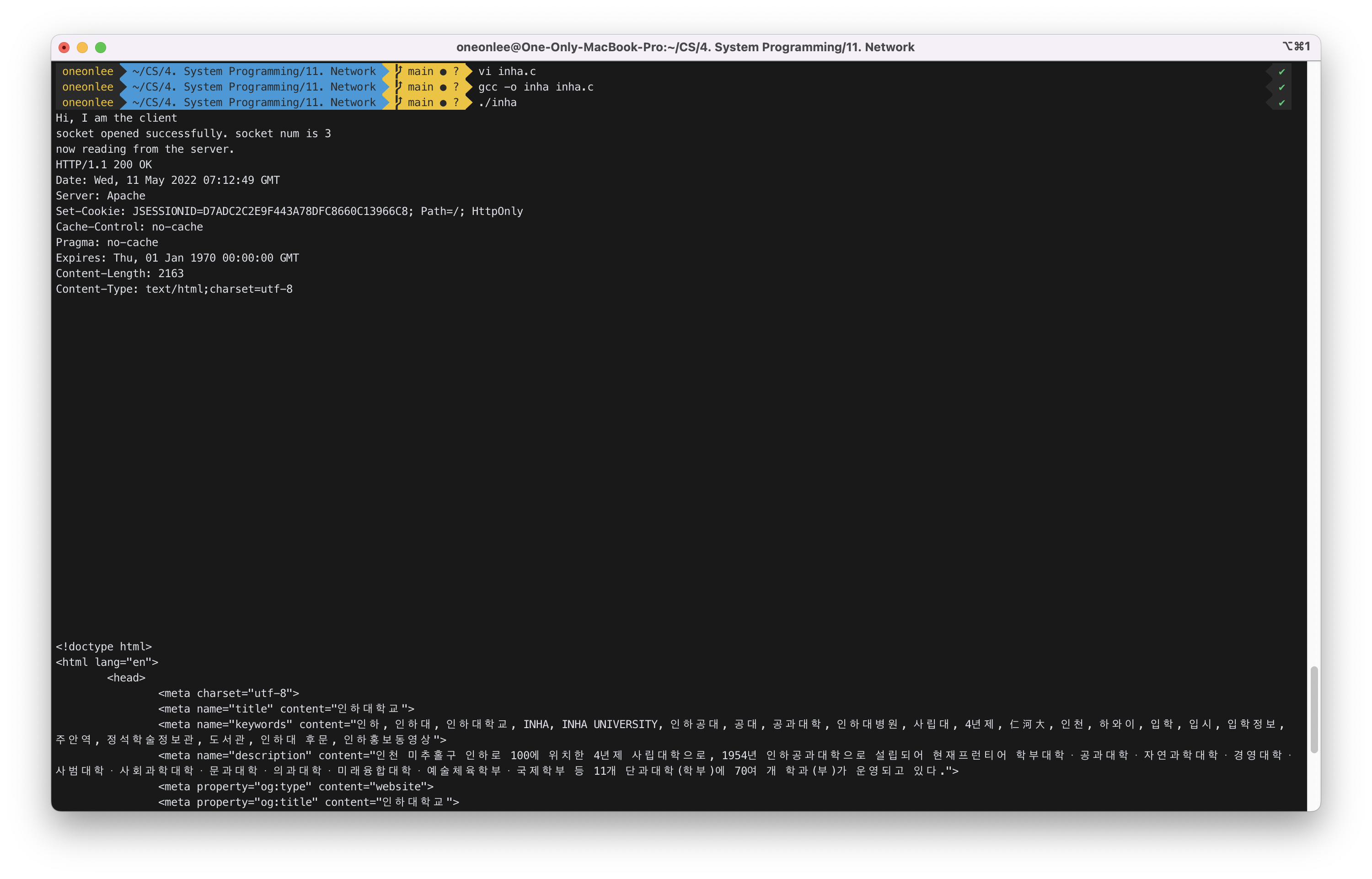
2-2) Modify cli.c such that it connects to Inha web server and read the web page. Inha web server domain name is www.inha.ac.kr and port number is 80. You can find the IP address for www.inha.ac.kr with ping command. To receive the web page from a web server, use GET command (your code should send below string automatically using write() function – do not type it by hand):
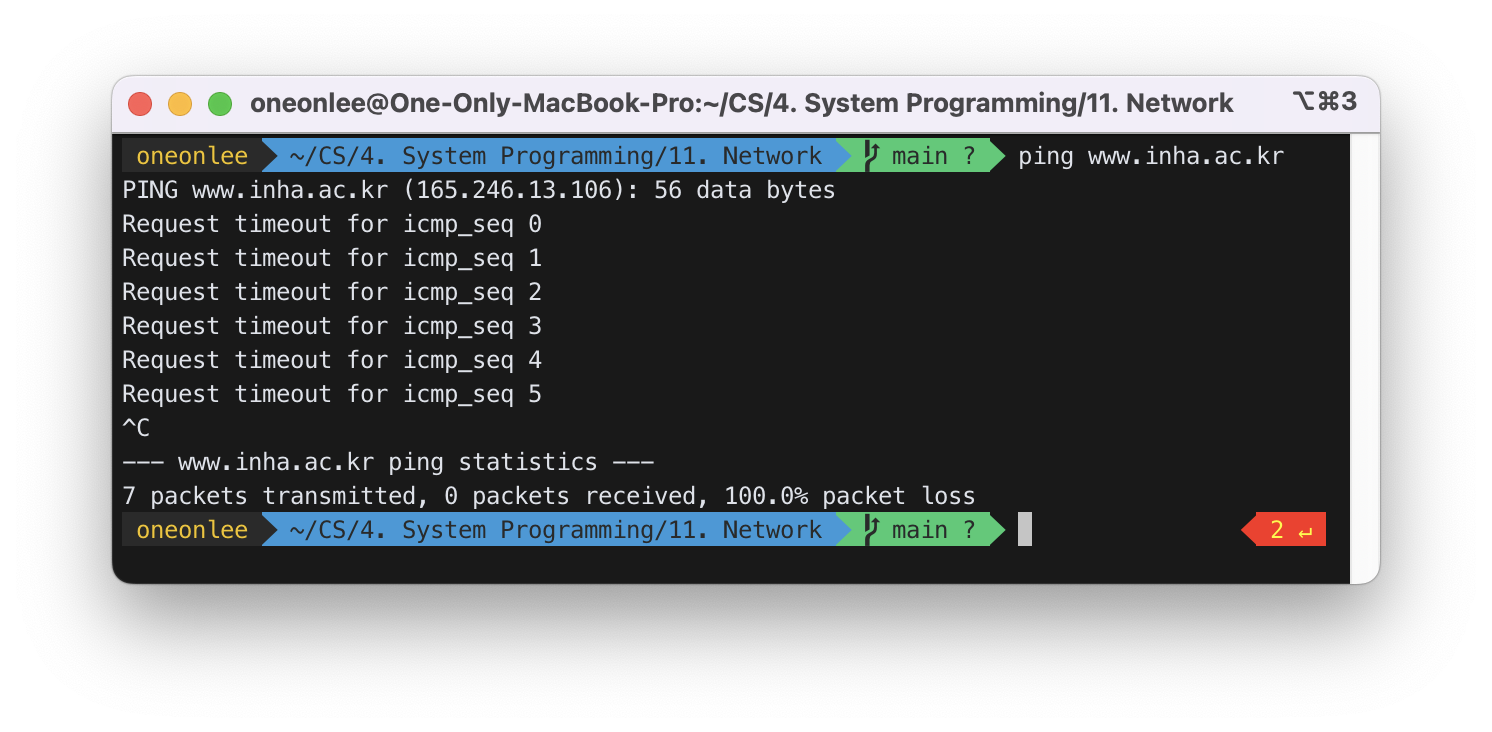
ping 명령어로 www.inha.ac.kr의 IP address를 확인한 결과 165.246.13.107임을 알 수 있었다.
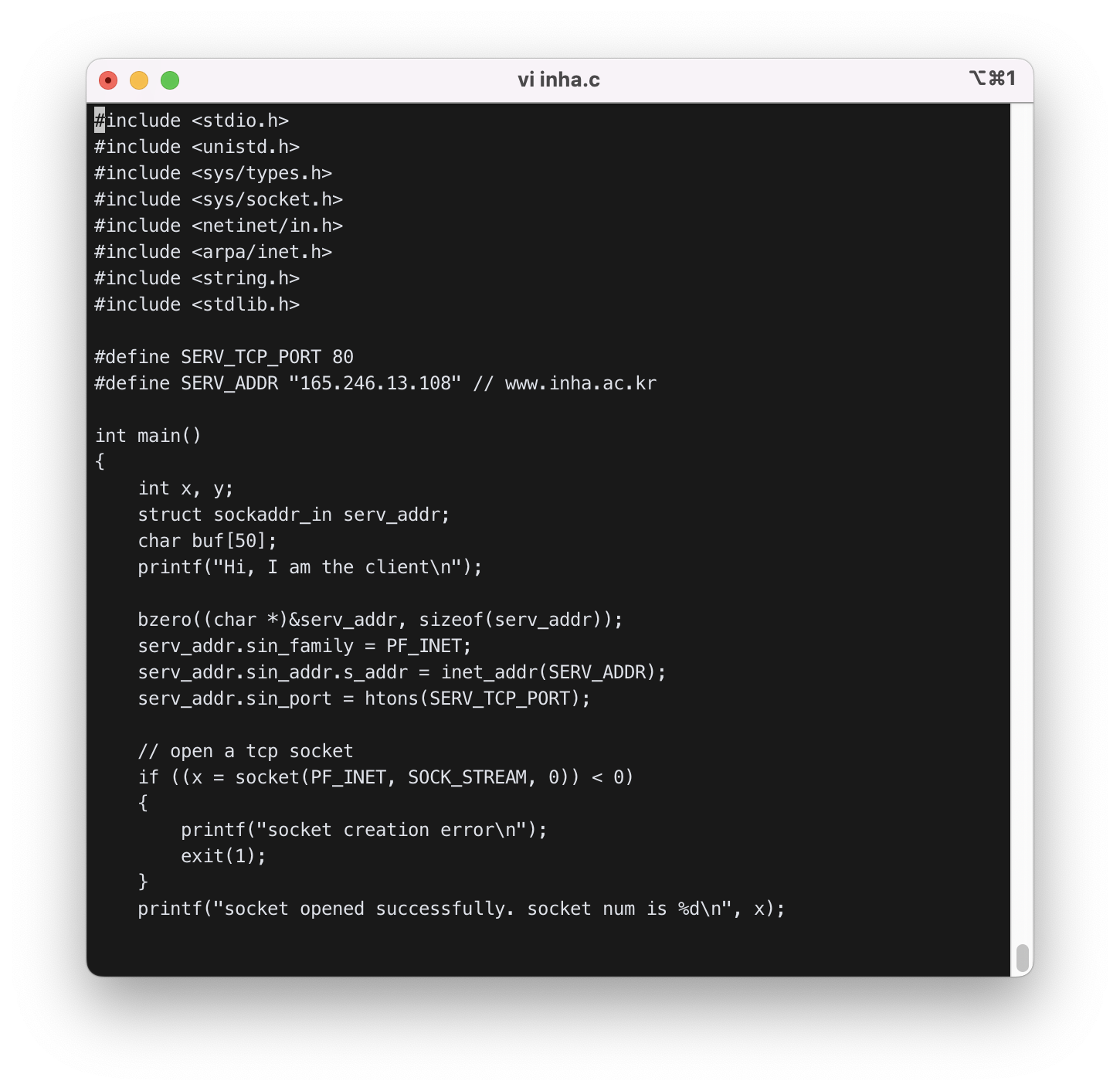
따라서 먼저, cli.c에서 define한 주소와 포트번호를 아래와 같이 수정해주었다.
#define SERV_TCP_PORT 80
#define SERV_ADDR "165.246.13.108" // www.inha.ac.kr
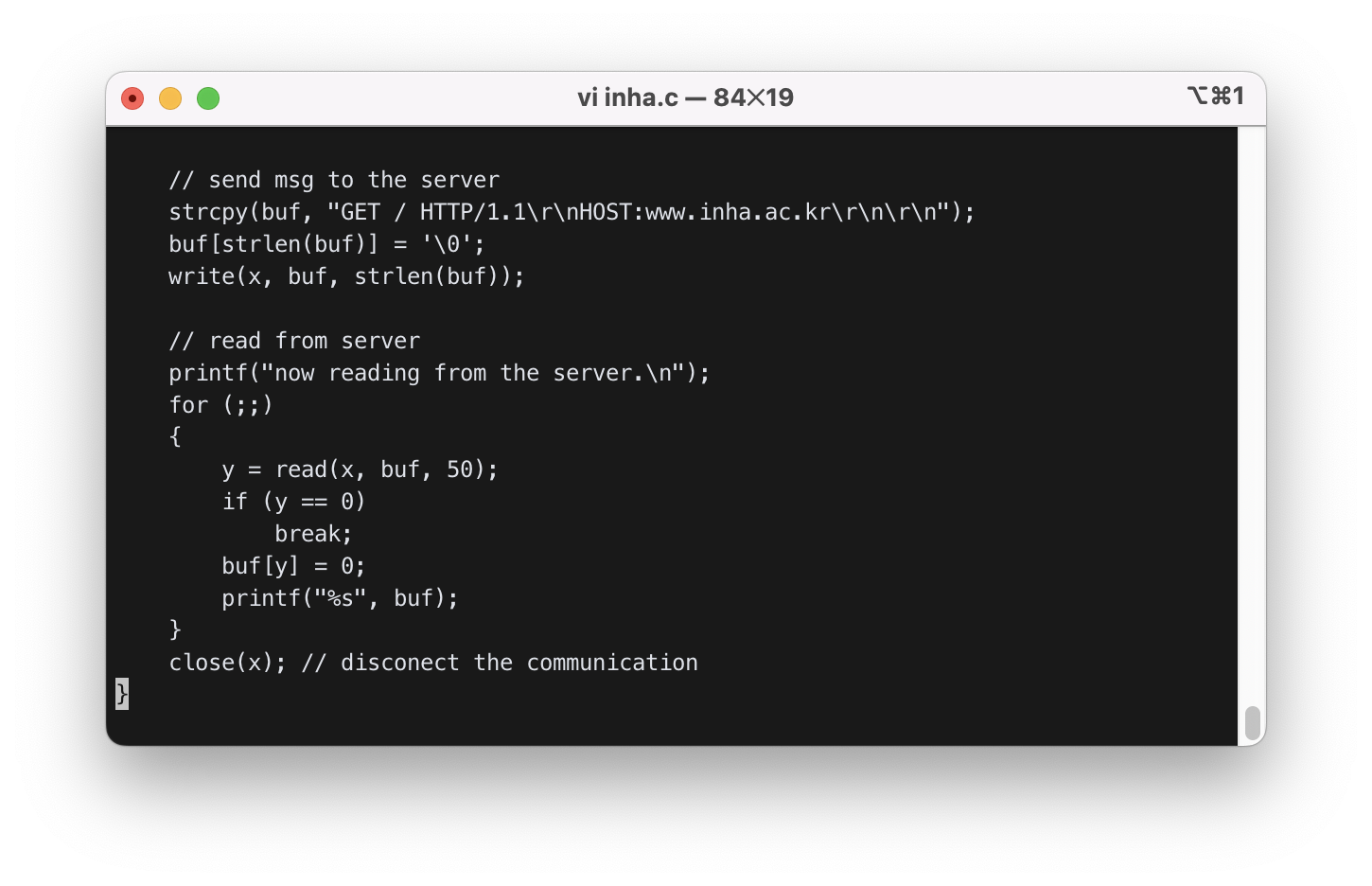
다음으로 서버에 메세지를 보낼 때, strcpy(buf, "GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHOST:www.inha.ac.kr\r\n\r\n");로 web page를 요청하였다.
// send msg to the server
strcpy(buf, "GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHOST:www.inha.ac.kr\r\n\r\n");
buf[strlen(buf)] = '\0';
write(x, buf, strlen(buf));
그리고 web page를 마지막까지 읽을 때까지 buf에 read하고 buf를 출력해서 보여준다.
// read from server
printf("now reading from the server.\n");
for (;;)
{
y = read(x, buf, 50);
if (y == 0)
break;
buf[y] = 0;
printf("%s", buf);
}
close(x); // disconect the communication
3) Modify the code such that the client and the server can talk in any order. Use a finite loop to avoid infinite number of processes.
serv.c
k = fork();
if (k == 0) // child will keep reading
{
printf("Now I am connected to the client.\n");
chpid = getpid();
// read msg from client
for (int c = 0; c < 10; c++)
{
y = read(s2, buf, 50 - 1);
buf[y] = '\0';
printf("Client : %s\n", buf);
if (strcmp(buf, "bye") == 0)
{
break;
}
}
kill(getppid(), 15); // kill parent process
}
else // parent keep writing
{
// send msg to the client
for (int p = 0; p < 10; p++)
{
// printf("Server : ");
fgets(buf, 50 - 1, stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
write(s2, buf, strlen(buf));
if (strcmp(buf, "bye") == 0)
{
kill(chpid, 15); // kill child process
break;
}
}
}
cli.c
k = fork();
if (k == 0) // child will keep writing
{
chpid = getpid();
// send msg to the server
printf("Now I am connected to the server.\n");
for (int c = 0; c < 10; c++)
{
// printf("Client : ");
fgets(buf, 50 - 1, stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
write(x, buf, strlen(buf));
if (strcmp(buf, "bye") == 0)
{
kill(getppid(), 15); // kill parent process
break;
}
}
}
else
{
// read from server
for (int p = 0; p < 10; p++)
{
y = read(x, buf, 50 - 1);
buf[y] = '\0';
printf("Server : %s\n", buf);
if (strcmp(buf, "bye") == 0)
{
break;
}
}
kill(chpid, 15); // kill child process
}
close(x); // disconect the communication
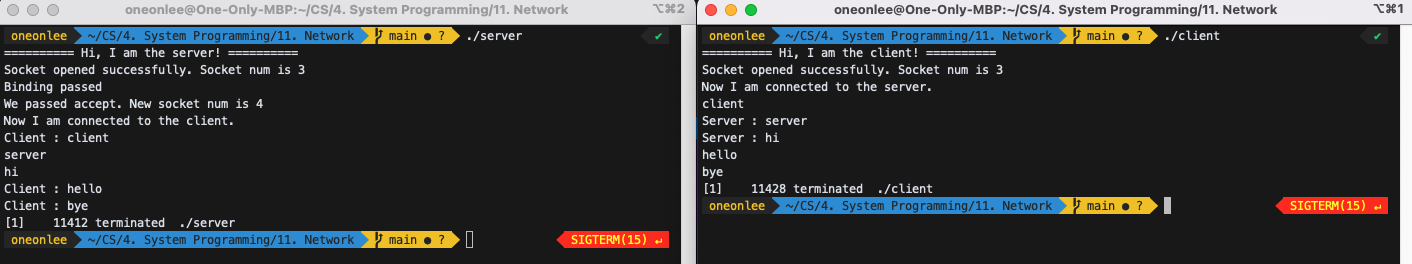
순서에 상관없이 server와 client간의 채팅을 할 수 있도록 수정하였다.
4) Implement simple ftp server and client. If the client doesn’t follow the protocol, the server should stop the communication. This is not chatting program. Do not type “hello”, “what file do you want?”, etc. The server and client should automatically send or receive the ftp protocol messages. The user will only provide the file name to download. Do not use the code from Problem 3, which will make the coding very hard. Modify the code from Problem 1.
Simple ftp protocol
client => server: hello
server => client: what file do you want?
client => server: file name
server => client: file contents
serv.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SERV_TCP_PORT 32330
#define SERV_ADDR "165.246.240.109"//"192.168.50.122"//"165.246.38.151"
int main(){
int s1,s2, x, y;
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr, cli_addr;
char buf[50];
char fileName[50];
socklen_t xx;
printf("Hi, I am the server\n");
bzero((char *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family=PF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr(SERV_ADDR);
serv_addr.sin_port=htons(SERV_TCP_PORT);
//open a tcp socket
if ((s1=socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0))<0){
printf("socket creation error\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("socket opened successfully. socket num is %d\n", s1);
// bind ip
x =bind(s1, (struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
if (x < 0){
printf("binding failed\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("binding passed\n");
listen(s1, 5);
xx = sizeof(cli_addr);
s2 = accept(s1, (struct sockaddr *)&cli_addr, &xx);
printf("we passed accept. new socket num is %d\n", s2);
// read msg from client
y=read(s2, buf, 50);
buf[y]=0;
printf("client => server: %s\n", buf);
if (strcmp(buf, "hello") == 0) {
char * init_response = "What file do you want?";
write(s2, init_response, strlen(init_response));
printf("server => client: %s\n", init_response);
wait(0);
// read name of the file from client
y=read(s2, fileName, 50);
fileName[y]=0;
printf("client => server: %s\n", fileName);
// send contents of the file
int fd = open(fileName, O_RDONLY, 00777);
for(;;) {
y = read(fd, buf, 50);
if (y==0) break;
buf[y] = '\0';
write(s2, buf, strlen(buf));
printf("%s", buf);
}
char * endString = "END";
write(s2, endString, strlen(endString));
}
close(s2); // disconnect the connection
close(s1); // close the original socket
return 0;
}
cli.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SERV_TCP_PORT 32330
#define SERV_ADDR "165.246.240.109"//"192.168.50.122"//"165.246.38.151"
int main(){
int x,y;
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr;
char buf[50];
printf("Hi, I am the client\n");
bzero((char *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family=PF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr(SERV_ADDR);
serv_addr.sin_port=htons(SERV_TCP_PORT);
//open a tcp socket
if ((x=socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0))<0){
printf("socket creation error\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("socket opened successfully. socket num is %d\n", x);
//connect to the server
if (connect(x, (struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)) < 0){
printf("can't connect to the server\n");
exit(1);
}
// send msg to the server
printf("client => server: ");
char * init_request = "hello";
write(x, init_request, strlen(init_request));
printf("%s\n", init_request);
// read from server
y=read(x, buf, 50);
buf[y]=0;
printf("server => client: %s\n", buf);
if (strcmp(buf, "What file do you want?") == 0) {
printf("client => server: ");
// send name of the file to the server
fgets(buf, 50, stdin);
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';
write(x, buf, strlen(buf));
// receive contents of the file
char * endString = "END";
printf("server => client: \n");
for(;;) {
y=read(x, buf, 50);
buf[y]='\0';
if (strcmp(endString, buf) == 0){
printf("\n");
break;
}
printf("%s", buf);
}
}
close(x); // disconect the communication
}
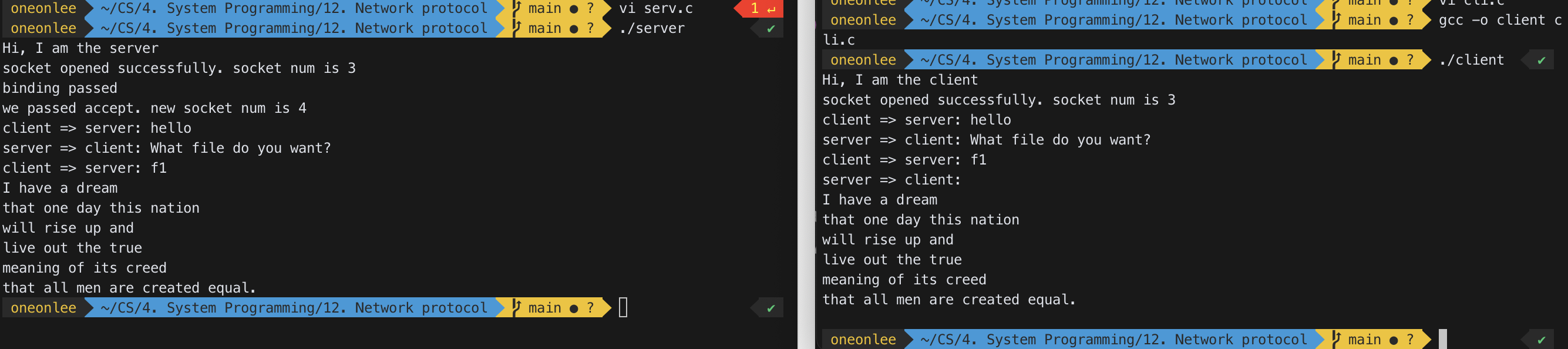
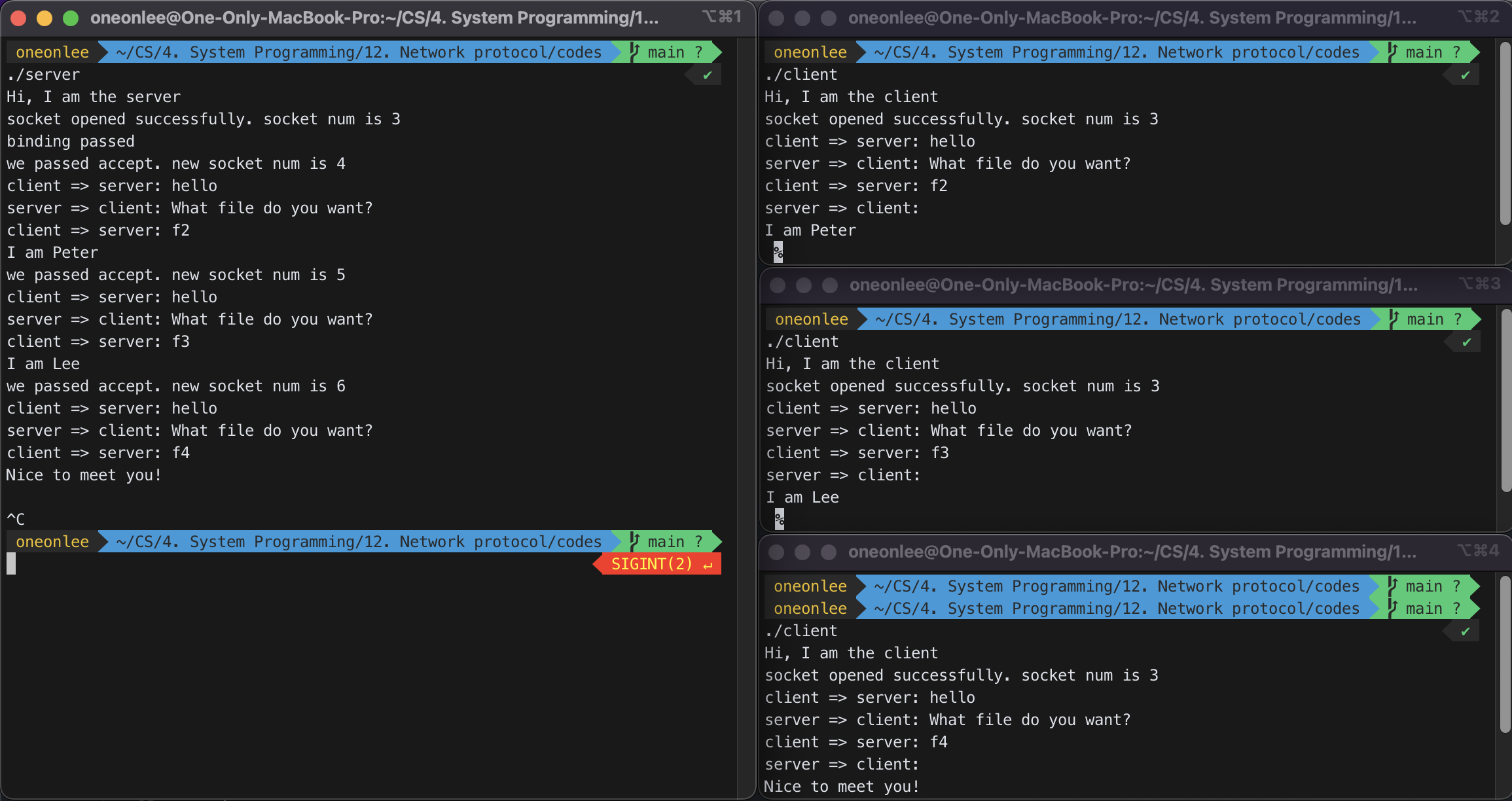
5) Modify your ftp server such that it can handle multiple clients at the same time.
serv.c
// open socket, bind, lisen
........................
// now wait for clients
for(i=0;i<20;i++){
s2=accept(s1, .............);
// now we have a new client. make a child to handle it
ch=fork();
if (ch==0){ // this child will handle the newly arrived client
// process simple ftp protocol
...............
close(s1);
close(s2);
exit(0); // child has completed the mission. exit now.
}
}
serv.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SERV_TCP_PORT 32330
#define SERV_ADDR "172.30.1.29"
int main()
{
int s1, s2, x, y, ch;
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr, cli_addr;
char buf[50];
char fileName[50];
socklen_t xx;
printf("Hi, I am the server\n");
bzero((char *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = PF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(SERV_ADDR);
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(SERV_TCP_PORT);
// open a tcp socket
if ((s1 = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0)
{
printf("socket creation error\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("socket opened successfully. socket num is %d\n", s1);
// bind ip
x = bind(s1, (struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
if (x < 0)
{
printf("binding failed\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("binding passed\n");
// listen
listen(s1, 5);
xx = sizeof(cli_addr);
// now wait for clients
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
s2 = accept(s1, (struct sockaddr *)&cli_addr, &xx);
printf("we passed accept. new socket num is %d\n", s2);
// now we have a new client. make a child to handle it
ch = fork();
if (ch == 0)
{ // this child will handle the newly arrived client
// process simple ftp protocol
// read msg from client
y = read(s2, buf, 50);
buf[y] = 0;
printf("client => server: %s\n", buf);
if (strcmp(buf, "hello") == 0)
{
char *init_response = "What file do you want?";
write(s2, init_response, strlen(init_response));
printf("server => client: %s\n", init_response);
wait(0);
// read name of the file from client
y = read(s2, fileName, 50);
fileName[y] = 0;
printf("client => server: %s\n", fileName);
// send contents of the file
int fd = open(fileName, O_RDONLY, 00777);
for (;;)
{
y = read(fd, buf, 50);
if (y == 0)
break;
buf[y] = '\0';
write(s2, buf, strlen(buf));
printf("%s", buf);
}
buf[0] = -1;
write(s2, buf, 1);
}
close(s2); // disconnect the connection
close(s1); // close the original socket
exit(0); // child has completed the mission. exit now.
}
}
return 0;
}
cli.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SERV_TCP_PORT 32330
#define SERV_ADDR "172.30.1.29" //"165.246.240.109"//"192.168.50.122"//"165.246.38.151"
int main()
{
int x, y;
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr;
char buf[50];
printf("Hi, I am the client\n");
bzero((char *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = PF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(SERV_ADDR);
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(SERV_TCP_PORT);
// open a tcp socket
if ((x = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0)
{
printf("socket creation error\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("socket opened successfully. socket num is %d\n", x);
// connect to the server
if (connect(x, (struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)) < 0)
{
printf("can't connect to the server\n");
exit(1);
}
// send msg to the server
printf("client => server: ");
char *init_request = "hello";
write(x, init_request, strlen(init_request));
printf("%s\n", init_request);
// read from server
y = read(x, buf, 50);
buf[y] = 0;
printf("server => client: %s\n", buf);
if (strcmp(buf, "What file do you want?") == 0)
{
printf("client => server: ");
// send name of the file to the server
fgets(buf, 50, stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
write(x, buf, strlen(buf));
// receive contents of the file
char *endString = "END";
printf("server => client: \n");
for (;;)
{
y = read(x, buf, 50);
buf[y] = '\0';
if (buf[y - 1] == -1)
{
buf[y - 1] = ' ';
printf("%s", buf);
break;
}
printf("%s", buf);
}
}
close(x); // disconect the communication
}
6) Write a client in your PC as follows and let it talk to the server program in the lab server. To compile the client program:
- Make an empty c++ project and copy the code given below.
- Adjust the server IP and port number
- Select
- “project->project property->manifest tools->input and output->include manifest” and set “No”
- add ws2_32.lib in project>project property>link>input>additional dependencies
- Select build->Solution Build
- You should see “Success 1” at the bottom of the compile window.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "winsock2.h"
#include "ws2tcpip.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#define SERVER_PORT 9924 // server port number
#define BUF_SIZE 4096 // block transfer size
#define QUEUE_SIZE 10
#define IPAddress "165.246.38.152" // server IP address
int main()
{
WORD wVersionRequested;
WSADATA wsaData;
SOCKADDR_IN target; //Socket address information
SOCKET s;
int err;
int bytesSent;
char buf[100];
//--- INITIALIZATION -----------------------------------
wVersionRequested = MAKEWORD( 1, 1 );
err = WSAStartup( wVersionRequested, &wsaData );
if ( err != 0 ) {
printf("WSAStartup error %ld", WSAGetLastError() );
WSACleanup();
return false;
}
//------------------------------------------------------
//---- Build address structure to bind to socket.--------
target.sin_family = AF_INET; // address family Internet
target.sin_port = htons (SERVER_PORT); //Port to connect on
inet_pton(AF_INET, IPAddress, &(target.sin_addr.s_addr)); // target IP
//--------------------------------------------------------
// ---- create SOCKET--------------------------------------
s = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP); //Create socket
if (s == INVALID_SOCKET)
{
printf("socket error %ld" , WSAGetLastError() );
WSACleanup();
return false; //Couldn't create the socket
}
//---------------------------------------------------------
//---- try CONNECT -----------------------------------------
if (connect(s, (SOCKADDR *)&target, sizeof(target)) == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
printf("connect error %ld", WSAGetLastError() );
WSACleanup();
return false; //Couldn't connect
}
//-------------------------------------------------------
//---- SEND bytes -------------------------------------------
printf("enter a string to send to server\n");
gets_s(buf, 99);
bytesSent = send( s, buf, strlen(buf), 0 ); // use "send" in windows
printf( "Bytes Sent: %ld \n", bytesSent );
// now receive
int n;
n=recv(s, buf, 50, 0); // read max 50 bytes
buf[n]=0; // make a string
printf("received: %s\n", buf);
//--------------------------------------------------------
closesocket( s );
WSACleanup();
return 0;
}
Client_win.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <ws2tcpip.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 100
#define SERV_ADDR "165.246.38.152"
#define SERV_PORT 13579
int main(void) {
printf("Hi, I am the client.\n");
WORD wVersionRequired = MAKEWORD(2, 2);
WSADATA wsaData;
int result = WSAStartup(wVersionRequired, &wsaData);
if (result != 0) {
printf("WSAStartup failed with error: %d\n", result);
return 1;
}
SOCKADDR_IN servAddr;
ZeroMemory(&servAddr, sizeof(servAddr));
servAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
servAddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
inet_pton(AF_INET, SERV_ADDR, &servAddr.sin_addr);
SOCKET connectSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
if (connectSocket == INVALID_SOCKET) {
printf("socket failed with error: %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
WSACleanup();
return 1;
}
if (connect(connectSocket, (SOCKADDR*) &servAddr, sizeof(servAddr)) == SOCKET_ERROR) {
printf("Unable to connect to server!\n");
closesocket(connectSocket);
WSACleanup();
return 1;
}
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
printf("Enter a string to send to server: ");
fgets(buf, BUFFER_SIZE, stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
int bytesSent = send(connectSocket, buf, (int) strlen(buf), 0);
printf("Bytes Sent: %d\n", bytesSent);
int bytesReceived = recv(connectSocket, buf, BUFFER_SIZE - 1, 0);
buf[bytesReceived] = 0;
printf("Received: %s\n", buf);
closesocket(connectSocket);
WSACleanup();
return 0;
}
Server(Linux):
$ ./server
Hi, I am the server.
Server socket(sfd=3) is created.
Client socket(cfd=4) is accepted.
receive: Hi, Linux
Hi, Windows
Client(Windows 10):
Hi, I am the client.
Enter a string to send to server: Hi, Linux
Bytes Sent: 9
Received: Hi, Windows
Windows에서는 시스템 콜 함수를 사용할 수 없다.
따라서 fopen과 같은 라이브러리 함수를 사용해야 한다.
recv와 send는 추가적으로 마지막 인자 flags를 받는데 이를 0으로 설정하면 아무 값도 설정하지 않은 것(기본값)을 취급된다.
또한, Windows의 소켓 프로그래밍에서는 WSAStartup와 WSACleanup을 프로그램 시작과 끝에 호출해야 한다.
7) Write an ftp client in your PC and let it talk to the ftp server you made in problem 5). Use this client to download a file from the lab server.
Client_win.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <ws2tcpip.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 100
#define SERV_ADDR "165.246.38.152"
#define SERV_PORT 13579
int main() {
WORD wVersionRequired = MAKEWORD(2, 2);
WSADATA wsaData;
int result = WSAStartup(wVersionRequired, &wsaData);
if (result != 0) {
printf("WSAStartup failed with error: %d\n", result);
return 1;
}
SOCKADDR_IN servAddr;
ZeroMemory(&servAddr, sizeof(servAddr));
servAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
servAddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
inet_pton(AF_INET, SERV_ADDR, &servAddr.sin_addr);
SOCKET connectSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
if (connectSocket == INVALID_SOCKET) {
printf("socket failed with error: %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
WSACleanup();
return 1;
}
if (connect(connectSocket, (SOCKADDR*) &servAddr, sizeof(servAddr)) == SOCKET_ERROR) {
printf("Unable to connect to server!\n");
closesocket(connectSocket);
WSACleanup();
return 1;
}
char* init_request = "hello";
send(connectSocket, init_request, (int) strlen(init_request), 0);
printf("client => server: hello\n");
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
int chunk = recv(connectSocket, buf, BUFFER_SIZE - 1, 0);
buf[chunk] = '\0';
printf("server => client: %s\n", buf);
recv(connectSocket, buf, 1, 0); // consume EOF character
while (1) {
printf("client => server: ");
fgets(buf, BUFFER_SIZE - 1, stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
send(connectSocket, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
if (strcmp(buf, "bye") == 0) {
break;
}
FILE* stream = fopen(buf, "w");
while (1) {
chunk = recv(connectSocket, buf, BUFFER_SIZE - 1, 0);
if (buf[chunk - 1] == -1) {
buf[chunk - 1] = '\0';
fprintf(stream, "%s", buf);
break;
} else {
buf[chunk] = '\0';
fprintf(stream, "%s", buf);
}
}
fclose(stream);
printf("server => client: File Downloaded.\n");
}
closesocket(connectSocket);
WSACleanup();
return 0;
}
Server(Linux):
$ ./server
Hi, I am the FTP server.
Server socket(sfd=3) is created.
Client socket(cfd=4) is accepted.
client => server: hello
server => client: What file do you want?
client => server: f1
server => client: I have a dream
that one day this nation
will rise up and
live out the true
meaning of its creed
that all men are created equal.
client => server: bye
Client(Windows 10):
client => server: hello
server => client: What file do you want?
client => server: f1
server => client: File Downloaded.
client => server: bye
Visual Studio 2019에서는 fopen 사용 시 컴파일 오류가 나기 때문에 전처리기에 _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 옵션을 줘서 해결해야 한다.
위에서 정의한 Simple FTP에서는 버퍼보다 큰 파일이 들어올 경우를 대비해 -1을 EOF 문자로 지정해 파일을 읽어오는데, init_request에 대한 응답으로 서버에서 읽어오는 값의 마지막 -1을 recv(connectSocket, buf, 1, 0);으로 지워줘야한다.
파일을 저장할 때는 fopen을 이용해 열고 fprintf으로 파일 내용을 작성했다.